Down syndrome, also known as trisomy 21, is a genetic disorder caused by the presence of all, or part of a third copy of chromosome 21. It is typically associated with physical growth delays, characteristic facial features, and mild to moderate intellectual disability.
The parents of the affected individual are typically genetically normal. The extra chromosome occurs by random chance. There is no known behavioral activity or environmental factor that changes the risk, but it is dependent on the age of the mother, increasing from less than 0.1% in 20 year-olds to 3% in those age 45. Down syndrome can be identified during pregnancy by prenatal screening followed by diagnostic testing, or after birth by direct observation and genetic testing. Since the introduction of screening, pregnancies with the diagnosis are often terminated. Regular screening for health problems common in Down syndrome is recommended throughout the person’s life.
Down syndrome is one of the most common chromosome abnormalities in humans. It occurs in about one per 1,000 babies born each year.
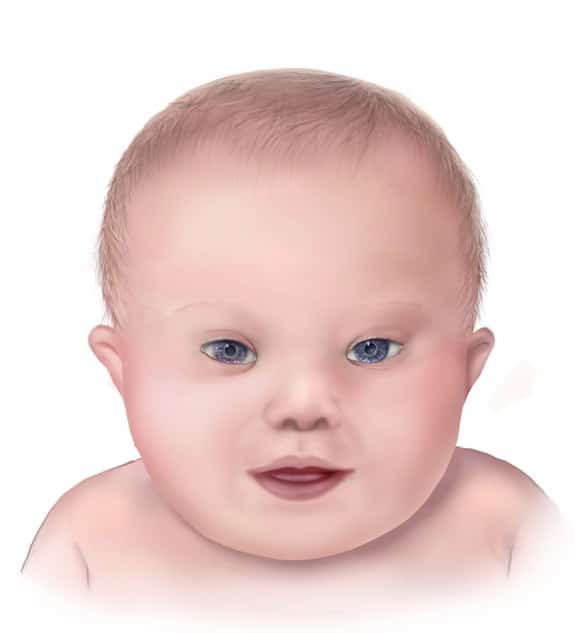
CDC Public Domain Image
For more info please visit:
National Down Syndrome Society
An organization that seeks to increase awareness and acceptance of those with Down syndrome.
http://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/birthdefects/DownSyndrome.html
Down syndrome. (2016, October 11). In Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia. Retrieved 21:01, October 11, 2016, from https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Down_syndrome&oldid=743887508
